Posted by Olivia dela Rosa on November 02, 2014
There are a lot of ways to print out images and texts these days, but not all of them can nail the job. For that, we look at some of the popular printing techniques and methods currently used and discover how they work and why we should use them.
Let us help you decide what type of printing method to choose for your next design project. While we're at it, let us also help you get the best printing deals and discounts in the market. Take a look at our wide selection of coupons and promotions with the major online printing companies.

According to Wikipedia "Letterpress printing is a technique of relief printing using a printing press"
Letterpress was invented in the 15th century and many people today think of Letterpress printing an "outdated process".
Fortunately a growing community of art enthusiasts and hobbyists are bringing this craftsmanship back to life. The process requires a high degree of craftsmanship and skill, and the results are stunning.
The process: In a gist, what happens during letterpress printing is basically called relief printing. It involves arranging movable types into a caddy, which were then arranged in reverse and locked into a chase to come up with the right spacing for the characters. These types have raised surface, which are inked and then repeatedly impressed against sheets or roll of paper.
Here’s a trivia: Did you know that Johannes Gutenberg was said to be the inventor of the first letterpress machine, and during the 15th century it was his machine that printed 180 copies of the Bible? I bet you didn’t. Only 48 copies remain to this day, and this only proves how significant the impact is of the letterpress during the old times up until now.
VIDEO: Just to have an idea of this kind of printing process, let Colt Bowden show you how it's done.




These are stills of Callil Capuozzo's letterpress printing process, after Solidsmack did an article about him and his works. (Video below)
The shift from hand-carved wooden blocks and other materials to metal type and image plates was due to the fact that the latter produces a much clearer print. It was only since the beginning of the 80’s that photo-polymer plates were used, which allowed letterpress shops to run a larger scaled print runs. The plates made it possible to make a digital design and translate it into a raised plate.
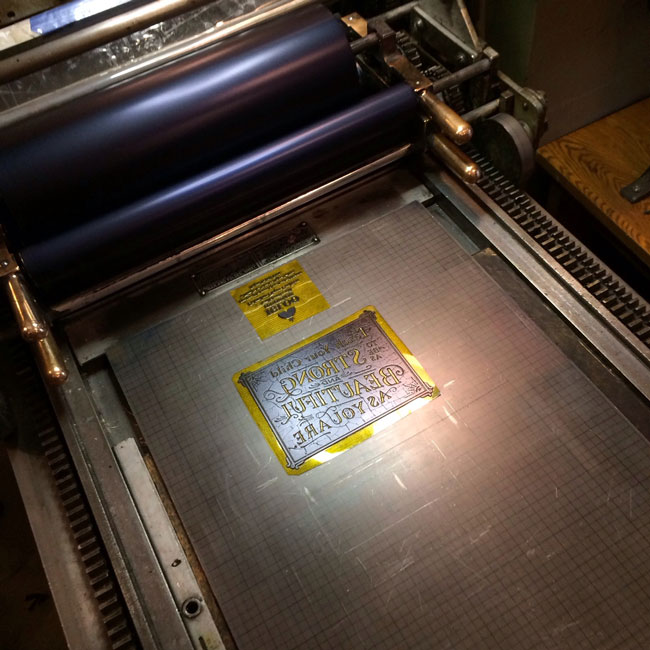
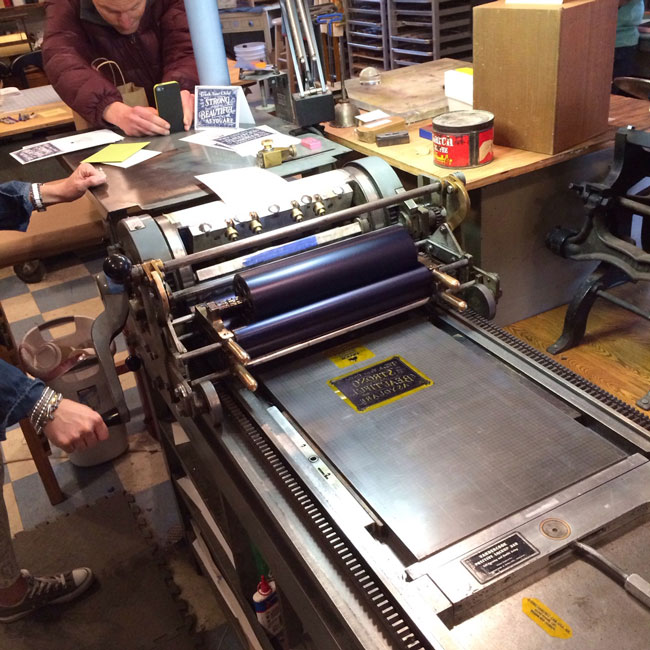



In his Behance profile, The Type Hunter showed us the art of letterpress using photo-polymers.
VIDEO: To better explain, here is a video of the process of letterpress printing. This particular piece is a part of Khalil Gibran's poem
Commonly used for: You probably have seen a lot of this for wedding invitations and business cards. Along with the evolution of letterpress technology, specialized papers were also invented to better suit the pressure from letterpress.
Why letterpress? The allure of letterpress lies in the tangible and tactile results that come out in every print. It reflects craftsmanship at its best, done after much thought, design and time put into it, thanks to the collaboration of artisans and designers who revived the vintage look. Most consider letterpress as more high quality than other techniques, and you see the design unfold right before your eyes, knowing and seeing how each part of the machine to print it out. Check the images below and see some examples of letterpress printing.



Business cards designed by James Prunean


Lithography, also known as offset printing, is usually the method used for commercial and mass printing. This type of print is mostly seen in product packaging, such as can labels, catalogues and brochures.
The process: Typically, the images are transferred from thin metal (often made of aluminum) plates to rubber blankets or rollers and then to paper or other materials with rougher surfaces, such as fabric, wood or canvas. It acts on the principle that ink and water don’t mix – these thin metal plates are dampened by rollers with water and ink, and the oil-based ink is then transferred to the image area only, into the rubber blanket and then passed on to the paper.
The metal plate does not come in direct contact with the paper: the lithography machine was designed as such to basically prolong the life of these plates, hence calling the process “offset”.
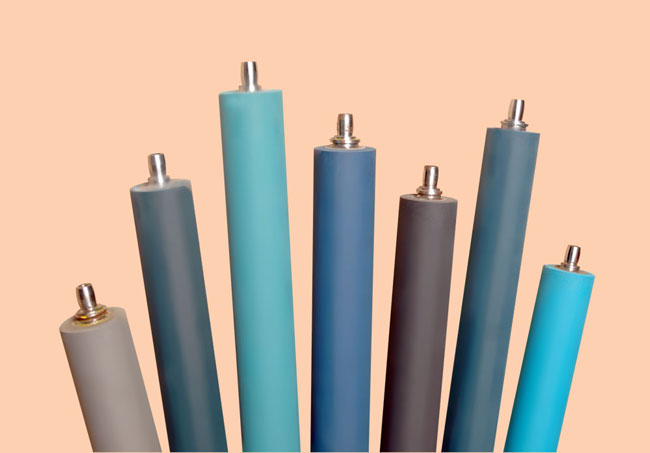

Various rollers used in offset lithography machines.

A closer look of lithography printing machine in action from Solopress.

Fausset Printing gives us a preview of the printing process.
VIDEO: Solopress made a video on how exactly offset lithography works, and it's kind of mesmerizing to watch the Heidelberg Speedmaster lithography machine do its job.
Commonly used for: Newspapers, posters, books, product labeling and packaging and such.
Why Offset Printing? Though the print is not something as tactile as letterpress, the quality and clarity of lithography is excellent. It works best with images and photographs with rich, vibrant colors and fine details. Offset lithography is often used in printing out publications, as well as promotion and packaging printing. It is also economically cheaper compared to digital printing if ordered in bulk, since the cost is really with the setup of the plates.
Benefits of Offset Printing
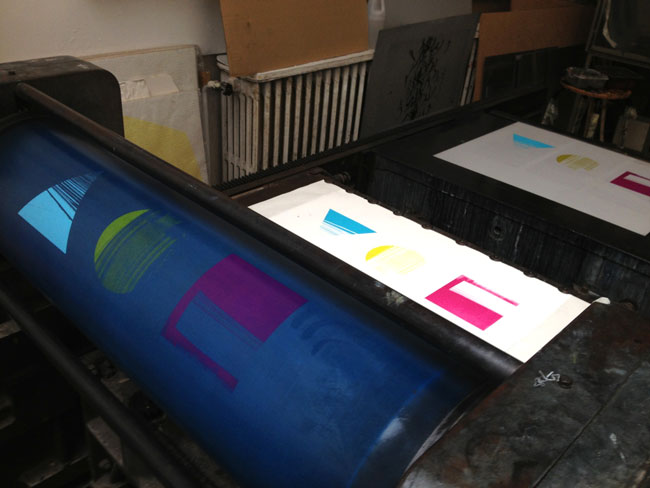




Breathing Out/Breathing In cover by Lee Basford

The most accessible of them all, digital printing is widely accepted as the printing method to use if you need something done instantly and accurately. No plates or machines are needed for this, so setup cost is low, and you just let the printer do all the work for you. Except perhaps feed it with paper.
The process: The image to be printed is prepared from the computer using graphics software such as Adobe Illustrator or InDesign. It is then sent to the printer, which in turn prints it out using toner and/or ink, depending on the type of printer you use. The toner sits on top of the paper rather than being absorbed by its fibers, and digital printing uses CMYK toner colors (cyan, magenta, yellow and black), which allows you to print just about any color that you can think of.
VIDEO: We all probably had encountered or even owned a digital printer at some point, so we know how it works, but let us show you one that is really made for high-speed and hiqh-quality printing. Nick Gossi posted a video of Neopost MACH 8S, an ink-jet digital printer that can print up to 60 ppm with a resolution of up to 1600x1600ppi.
Commonly used for: There are two types of digital printers; the ink-jet and laser printers. The latter uses laser beams, toner and heat to print the image onto the paper, while the first one uses ink, which is sprayed from the cartridges on to the paper. In general Inkjets are deemed much better in handling photographs and the laser printer has better quality when printing out type and graphics.
Why digital printing? Since it requires no plates, digital printing makes it possible to print individual and unique designs at relatively low costs. It enables you to print with multiple colors and offers high quality end results. If you need to print low volume ( like 100 flyers) or if each print requires a unique code or element to the design, digital printing is the best option for you.
Benefits of Digital Printing


Here & There poster by Marisa Midori via Etsy

Wired by Trois.Lee

Happy Land by Yu Rong

Flexography (or roll-to-roll or roll label printing) is the "modern version" of offset printing. Flexography is a printing technique that uses relief plates, which are then wrapped around rotating cylinders. The main tool it utilizes here is either a flexible relief plate – thin sheets of polymer material coated with a photosensitive surface – or natural or synthetic rubber. Flexographic printing, sometimes referred to as surface printing, is known for its commercial use, as the process can accommodate printing on a continuous roll of print media instead of doing it per sheet.
The process: The power of flexography lies in its ability to print even on uneven surfaces. Unlike the ones used in offset lithography, flexography uses thin metal or rubber plates with slightly raised surface, which are then rotated on a cylinder and in the process transfers the images onto the print media of choice. The plate is painted with water-based fast-drying inks that have low viscosity and make them perfect not only for paper but also any type of absorbent and non-absorbent materials, such as plastic, foil, acetate film and such. These fast-drying inks also allow one to print at a high speed, suitable for mass-produced printing process.
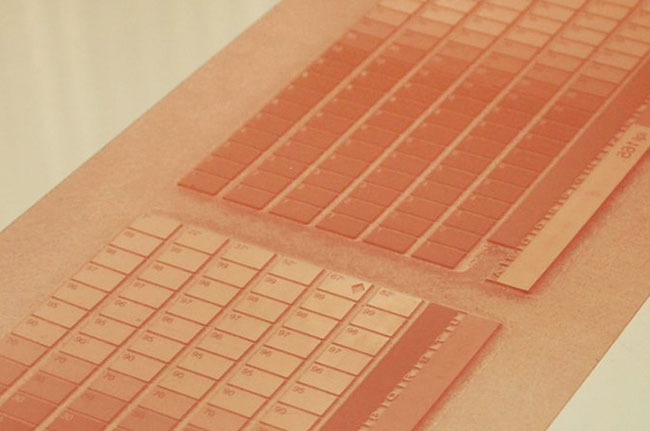
Photopolymer plates from Rapidoplex
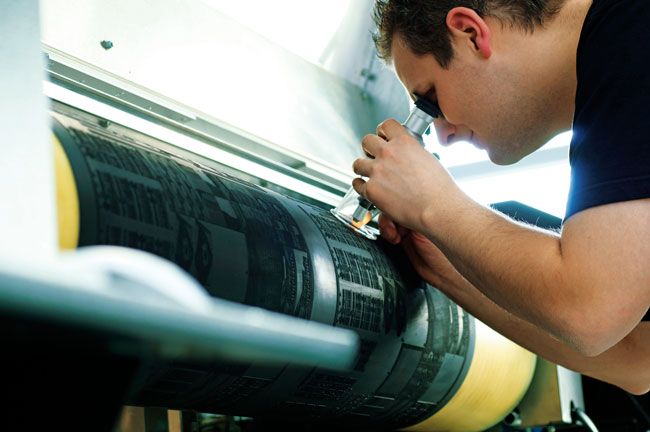

Flexo printing plates are checked for quality for precision.
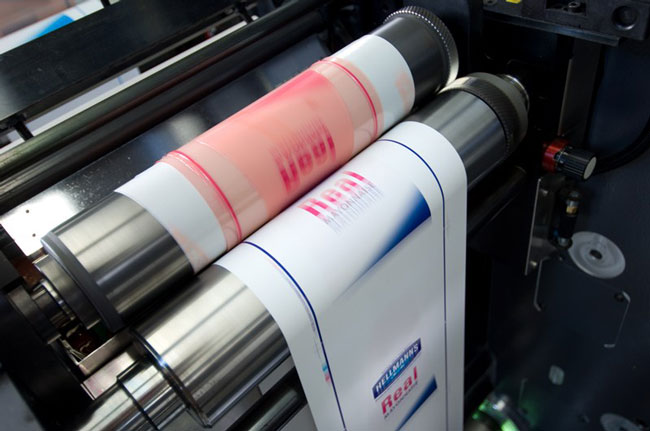

A preview of the flexographic printing machine in action.
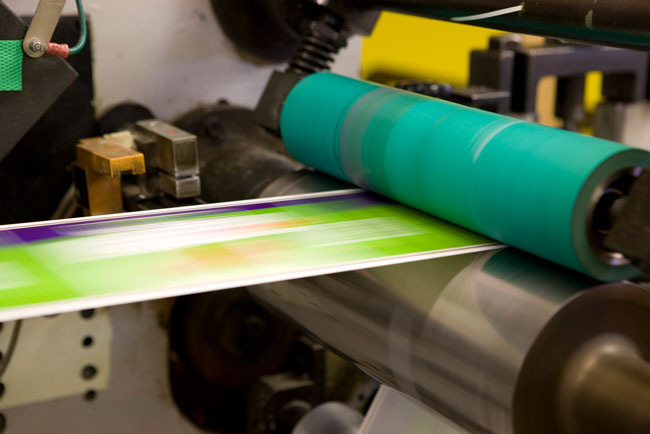

This is what high-speed printing looks like through flexography.
VIDEO: For something that could handle big printing production, it's intriguing how it's all done. To help us, a Youtube video by Kat Fish explains to us the whole process of flexography.
Commonly used for: Product packaging and labels, high-volume prints like newspapers, and printed products with continuous patterns like wallpaper and gift-wrap.
Why flexography? Best to consider using this type of printing technique for large-scaled print production because of its easy plate-making process. Flexography also lets you print on both porous and non-porous materials, from surfaces like plastic and foil, even floor tiles. If you’re in the edible goods business, flexography is the best option: The printing is bonded to the packaging surface, which guarantees safety and without having to worry about it wearing off, chipping or flaking and eventually harming the food.
Benefits of Flexography Printing:
Village Farms packaging
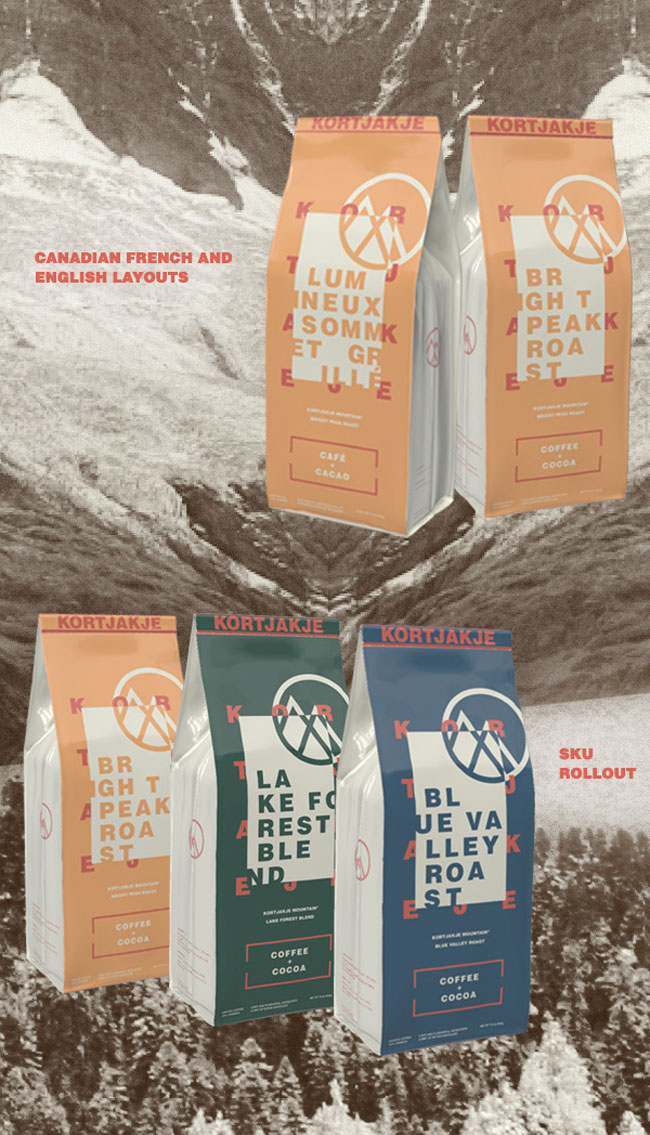

Kortjakje Mountain Coffee packaging designed by Frank JE Flitton
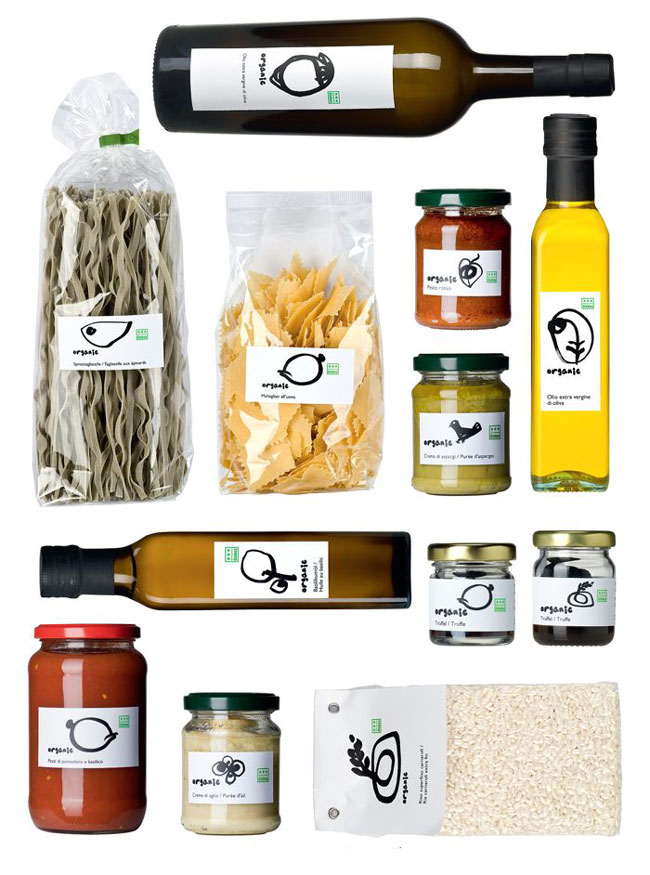

Globus Organics labeling and packaging
A lot of things need to be considered when choosing the right printing method to use: the substrate, the color mode, the number of colors of the design, resolution, volume, surface, desired effect, budget and others. Each of these factors are at play when choosing the best printing method for your design. This post touches only the surface of the available printing methods today but it should give you an idea of the available options.
Our advise is to seek the help of a print expert if you want the best possible results for your design. Most of the large printing companies offer multiple in-house printing techniques and will gladly offer free advise if you decide to order with them
The Future of Print - Digital Print Ads
Graphic Design Trends in 2014
Common Printing Mistakes to avoid
|
Dear Madam, Very use full, gathered information....thanks a lot..... Posted on February 16, 2015 by vinu.K.P |

Inkgarden offers the most flexibility with their design tools. You can actually save your design to complete it later, and their tools allow you to exactly position where the design is located on the product that you create. Adding text is easy, you can use multiple designs, choose if you want to use single or double sided, etc, etc.
Product quality was satisfying, and customer service was helpful.
I will definately use them again.
 Rating: 5 / 5
Rating: 5 / 5
Moo businesscards rock! Only downside is their price. Previously i ordered from a local printshop that was slightly cheaper but not even close to Moo's quality and luxurious feel
 Rating: 5 / 5
Rating: 5 / 5
We use Vistaprint for all our printing work. They are reliable and offer great quality print work for very good prices (especially if you use their discount coupons).
For us, Vistaprint is a reliable partner.
 Rating: 5 / 5
Rating: 5 / 5
These guys are the absolute best! I have a ton of stuff ordered from them: last week I received a photobook I ordered for my niece, it looked perfect, very professional and her mother loved it. Acrylic prints, canvas prints, everything you order from there is super high quality and reasonably priced.
 Rating: 5 / 5
Rating: 5 / 5
I love Cafepress, this company has the best customer service: My sister ordered a printed sweatshirt for my son from them. Unfortunately it didn't fit him (the sweatshirt was to large). We contacted RMA and within a few hours they replied: we will send you a new one in the correct size. we didn't have to ship the old one back, which saved me postage and a trip to the postoffice. I never had this happen before, very impressed by Cafepress!
 Rating: 5 / 5
Rating: 5 / 5
